Describe the Structure and Use of Cartilage Within Joints
Articular cartilage is the highly specialized connective tissue of diarthrodial joints. The muscles are attached to the bones via rope-like structures called tendons.
Most diarthrodial joints in the body are classified as ovoid.
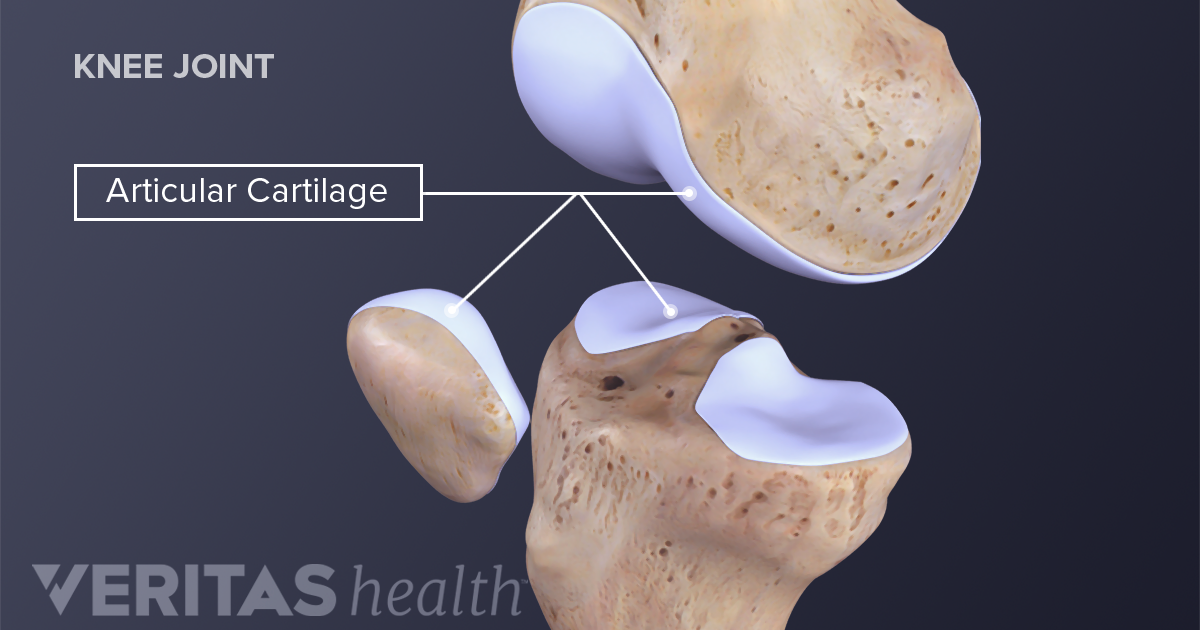
. The most common place you will find cartilage is in joints such as the knee and between the ribs to protect the lungs and heart. Joints between bones eg. Cartilage has many functions including the ability to resist compressive forces enhance bone resilience and provide support on bony areas where there is a need for flexibility.
An ovoid joint has one articular surface that is convex and another that is concave. Cartilage also smoothens the bone surfaces at the joints. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that protects your body from injury and aids in movements.
Cartilage is a robust and viscoelastic connective tissue that can be found in joints between bones the rib cage intervertebral discs the ear and the nose. The more common name for this type of cartilage is articular cartilage. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone.
Provide an anatomic example of each type of joint. With a pliable structure composed primarily of water this tissue type is also extremely tough. These types of joints lack a joint cavity and involve bones that are joined together by either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage Figure.
It comprises the outer ear some of the nose and trachea. The meniscus in the knee joint is made of half-moon-shaped fibrocartilage and so is the ring. The second type of cartilaginous joint is a symphysis where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage.
Cartilaginous joints are specialized types of joints which are classified based on their structure. Rubber-like padding that covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints elastin. These joints are mainly involved in a slight movement which lacks a joint cavity and comprises bones that are joined together either by fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage.
A synchondrosis is a cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage. The term articular cartilage does not refer to the type of cartilage structure but to its location. This causes it to heal very slowly.
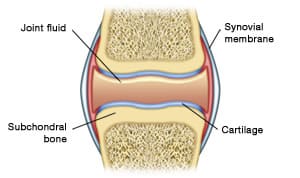
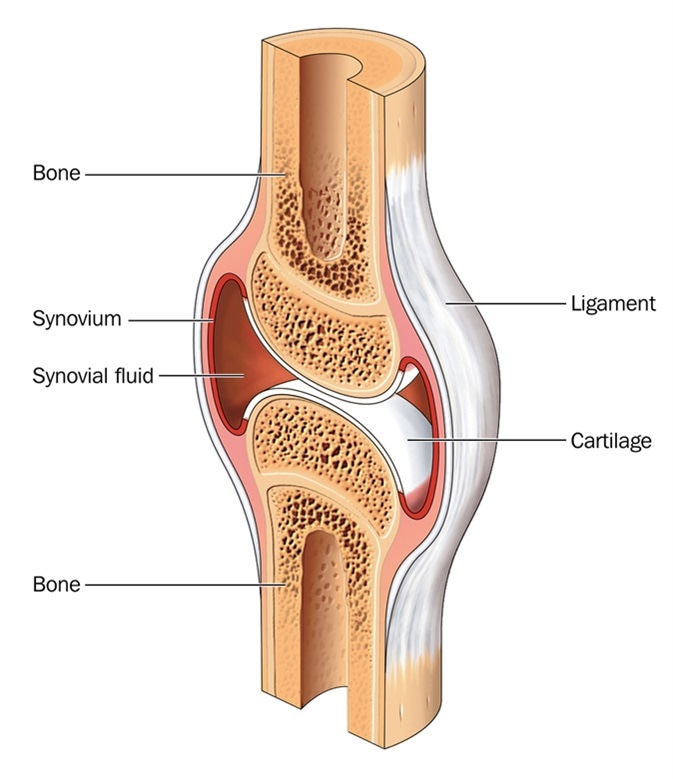
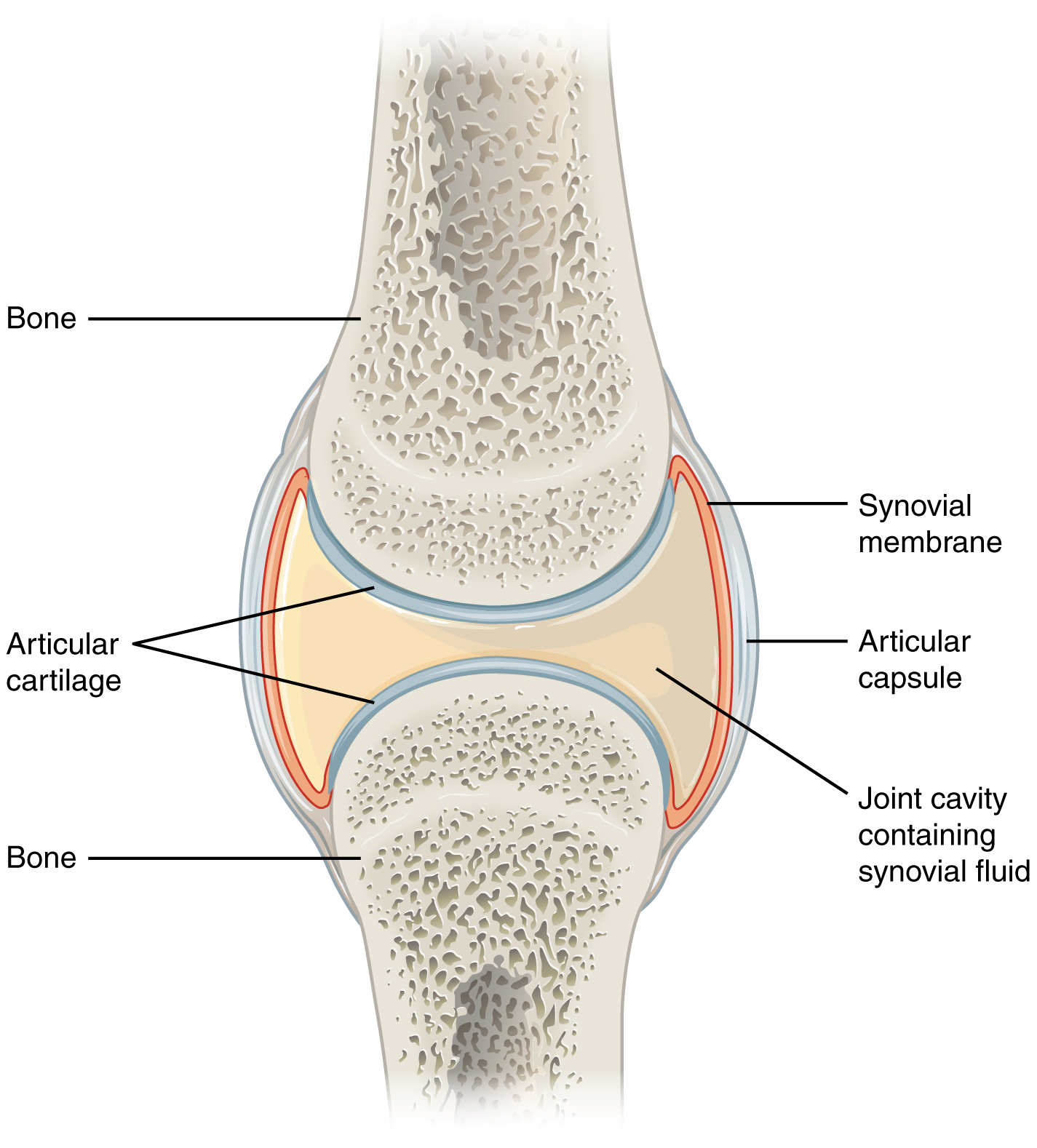
Articular cartilage is devoid of blood vessels lymphatics and nerves and is subject to a harsh biomechanical environment. ARTICULAR CARTILAGE hyaline cartilage covering epiphysis joint surface PERFORATING FIBERS collagen fibers anchor periosteum to bone NUTRIENT FORAMINA foramina for blood vessels NUTRIENT CANAL culminating passageway for nutrient arteriesveins from all nutrient foramina found in long and irregular bones. Cartilage gives shape support and structure to other body tissues.
Hyaline cartilage is prevalent throughout our bodies. Articular cartilage locations are found throughout the body. It is firmly anchored to the bone and is responsible for the fluid movement of the bones in a joint.
It also helps to cushion joints. The cartilage helps in keeping the bones from rubbing together and protects our spinal cord. Cartilaginous joints growth plates the symphysis the spine and the ribs have very little movement and no synovial membrane.
Its principal function is to provide a smooth lubricated surface for articulation and to facilitate the transmission of loads with a low frictional coefficient Figure 1. At cartilaginous joints bones are united by hyaline cartilage to. Cartilage is a fascinating substance.
There are two types of cartilaginous joints. Cartilage is found throughout the human body in areas such as the joints nose airway intervertebral discs of the spine and the ear. Also classified as a synchondrosis are places where bone is united to a cartilage structure such as.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways. Cartilage provides structure and protects our organs. The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte which resides within the lacunae.
The anatomy of our musculoskeletal system is quite complex. There are two types of cartilaginous joints. It contains mostly collagen fibers.
It is essential for the development and growth of long bones. As per the name cartilaginous joints are involved in uniting the. Cartilage is a semi-rigid but flexible avascular connective tissue found at various sites within the body.
Figure 931 Cartiliginous Joints. The matrix of cartilage consists of fibrous tissue and various combinations of proteoglycans and. It coats the ends of our bones allowing them to glide by one another at joints like our elbows and our.
The elbows knees and ankles. We are able to control our muscles by sending stimulating impulses via nerves from our brain. The joint between the manubrium and the sternum is.
Form the structure of body parts like our ears and windpipe. Fibrous joints skull sutures dental sockets and other immovable joints have no. Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that gives strength and elasticity to joint bones and protects the bones.
Cartilage is a connective tissue found in many areas of the body including. Fibrocartilage is a flexible elastic tough form of cartilage that provides cushioning in the joints. Fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone.
Between the vertebrae in the spine. Cartilage is not innervated and therefore relies on diffusion to obtain nutrients. Offering flexibility and support it.
Cartilaginous joints are connected entirely by cartilage fibrocartilage or hyaline. The cartilage aids in the cushioning of the skeletal system and even holds all the joints together. While more rigid and less flexible than muscle cartilage is not as stiff as bone.
Cartilage in your joints helps to cushion lubricate and provide flexibility to your movements. It has an appearance similar to that of the brain and the spinal cord. Three types of cartilage reside in the body.
Ends of the ribs. Protein of the extracellular matrix which is highly elastic tendon. There are three different types of cartilage in the body.
Describe the morphologic differences between ovoid and saddle joints. Fibrocartilage is tough and inflexible located between vertebrae in the knees hip and pelvis. Cartilage is formed of tiny cells called chondrocytes and is surrounded by a thin transparent membrane.
The cartilage is an elastic framework which allows our bones to adjust their positions. Cartilage is made up. A synchondrosis is a cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage or where a bone is united to hyaline cartilage.
Cartilaginous joints allow more movement between bones than a fibrous joint but less than the highly mobile synovial joint. Elastic cartilage is supple and flexible. Bronchial tubes or airways.
It consists of a large number of tendons ligaments bones cartilage joints and bursae.
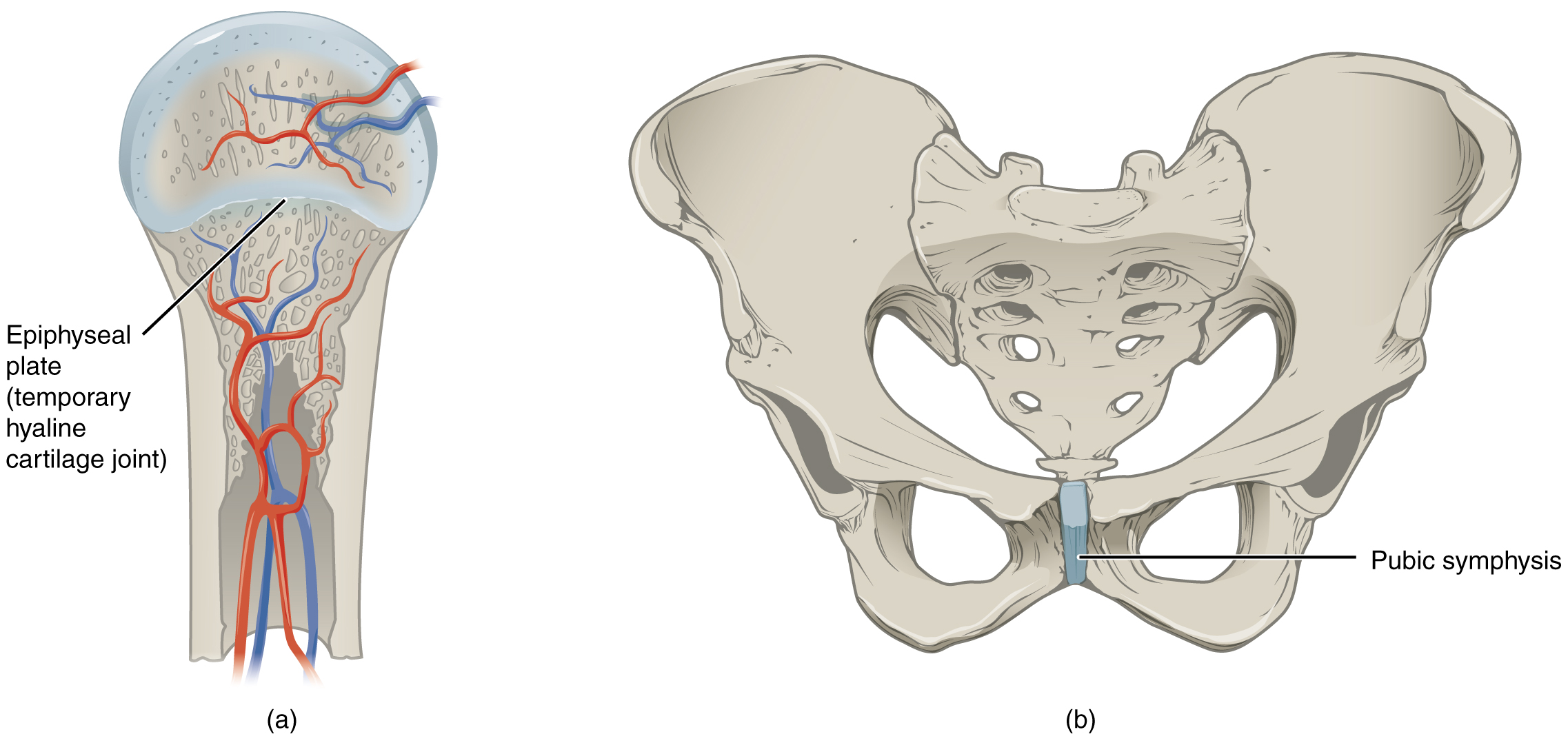
Cartilaginous Joints Anatomy And Physiology
Comments
Post a Comment